VMware
The following are some architectural highlights of Kubernetes clusters provisioned by Palette on VMware:
- Kubernetes nodes can be distributed across multiple-compute clusters, which serve as distinct fault domains.
- Support for static IP as well as DHCP. If your are using DHCP, Dynamic DNS is required.
- IP pool management for assigning blocks of IPs dedicated to clusters or projects.
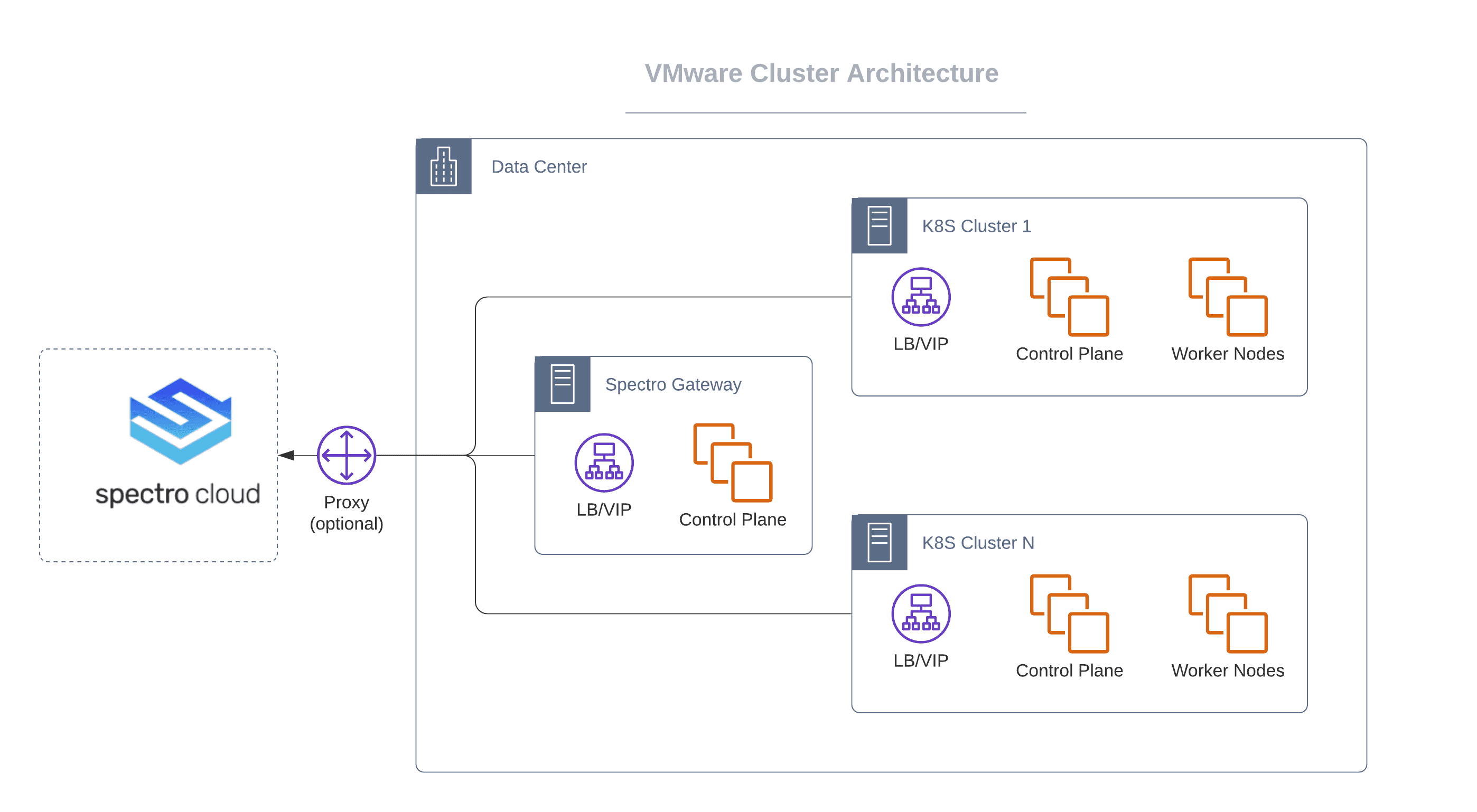
A Private Cloud Gateway (PCG) that you set up within the environment facilitates communications between the Palette management platform and vCenter installed in the private data center.
The PCG is Palette's on-prem component to enable support for isolated, private cloud, or data center environments. When the PCG is installed on-prem, it registers itself with Palette's SaaS portal and enables secure communications between the SaaS portal and private cloud environment.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites must be met before deploying a Kubernetes clusters in VMware:
vSphere version 7.0 or above. vSphere 6.7 is supported but we do not recommend it, as it reached end of general support in 2022.
Palette supports port groups as follows. Opaque networks in vCenter Server are not supported.
- Virtual machine port groups on vSphere standard switch
- Distributed port groups on vSphere distributed switch
- NSX-T distributed virtual port group
- A Resource Pool configured across the hosts onto which the workload clusters will be provisioned. Every host in the Resource Pool will need access to shared storage, such as vSAN, to be able to make use of high-availability (HA) control planes.
- Network Time Protocol (NTP) configured on each ESXi host.
- An active vCenter account with all the permissions listed in VMware Privileges.
- Installed PCG for VMware. Installing the PCG will automatically register a cloud account for VMware in Palette. You can register your additional VMware cloud accounts in Palette as described in the Create VMware Cloud Account section.
A subnet with egress access to the internet (direct or via proxy):
- For proxy: HTTP_PROXY, HTTPS_PROXY (both required).
- Outgoing internet connection on port 443 to api.spectrocloud.com.
PCG IP requirements are:
- One node with one IP address or three nodes for HA with three IP addresses.
- One Kubernetes control-plane (VIP).
- One Kubernetes control-plane (extra).
- IPs for application workload services, such as LoadBalancer service.
- A DNS to resolve public internet names, such as
api.spectrocloud.com.
- Shared Storage between vSphere hosts.
- A cluster profile created in Palette for VMWare.
- Zone tagging for dynamic storage allocation for persistent storage.
The following naming conventions apply to vSphere Region and Zone tags:
- Valid tags consist of alphanumeric characters.
- Tags must start and end with an alphanumeric character.
- The regex used for validation is
(([A-Za-z0-9][-A-Za-z0-9_.]*)?[A-Za-z0-9])?
Some example Tags are: MyValue, my_value, and 12345.
Zone Tagging
Zone tagging is required for dynamic storage allocation across fault domains when you provision workloads that require persistent storage. This is required for Palette installation and useful for workloads deployed in tenant clusters that require persistent storage. Use unique vSphere tags on data centers (k8s-region) and compute clusters (k8s-zone) to create distinct zones in your environment. Tag values must be unique.
For example, assume your vCenter environment includes three compute clusters (cluster-1, cluster-2, and cluster-3) that are part of data center dc-1. You can tag them as follows:
| vSphere Object | Tag Category | Tag Value |
|---|---|---|
| dc-1 | k8s-region | region1 |
| cluster-1 | k8s-zone | az1 |
| cluster-2 | k8s-zone | az2 |
| cluster-3 | k8s-zone | az3 |
VMware Privileges
The vSphere user account that deploys Palette must have the minimum root-level vSphere privileges listed in the table below. The Administrator role provides superuser access to all vSphere objects. For users without the Administrator role, one or more custom roles can be created based on tasks the user will perform. Permissions and privileges vary depending on the vSphere version you are using.
Select the tab for your vSphere version.
If the network is a Distributed Port Group under a vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS), ReadOnly access to the VDS without “Propagate to children” is required.
- 8.0
- 7.0
- 6.7
Root-Level Role Privileges
Root-level role privileges listed in the table are applied only to root objects and data center objects.
| vSphere Object | Privileges |
|---|---|
| Cns | Searchable |
| Datastore | Browse datastore |
| Host | Configuration |
| * Storage partition configuration | |
| vSphere Tagging | Create vSphere Tag |
| Edit vSphere Tag | |
| Network | Assign network |
| Sessions | Validate session |
| VM Storage Policies | View VM storage policies |
| Storage views | View |
Spectro Role Privileges
The Spectro role privileges listed in the table must be applied to the spectro-template folder, hosts, clusters, virtual machines, templates, datastore, and network objects.
Palette downloads images and Open Virtual Appliance (OVA) files to the spectro-templates folder and clones images from it to create nodes.
| vSphere Object | Privileges |
|---|---|
| spectro-templates | Read only |
| Cns | Searchable |
| Datastore | Allocate space |
| Browse datastore | |
| Low-level file operations | |
| Remove file | |
| Update virtual machine files | |
| Update virtual machine metadata | |
| Folder | Create folder |
| Delete folder | |
| Move folder | |
| Rename folder | |
| Host | Local operations |
| Reconfigure virtual machine | |
| vSphere Tagging | Assign or Unassign vSphere Tag |
| Create vSphere Tag | |
| Delete vSphere Tag | |
| Edit vSphere Tag | |
| Network | Assign network |
| Resource | Apply recommendation |
| Assign virtual machine to resource pool | |
| Migrate powered off virtual machine | |
| Migrate powered on virtual machine | |
| Query vMotion | |
| Sessions | Validate session |
| VM Storage Policies | View VM storage policies |
| Storage views | Configure service |
| View | |
| Tasks | Create task |
| Update task | |
| vApp | Export |
| Import | |
| View OVF environment | |
| vApp application configuration | |
| vApp instance configuration | |
| Virtual machines | Change Configuration |
| * Acquire disk lease | |
| * Add existing disk | |
| * Add new disk | |
| * Add or remove device | |
| * Advanced configuration | |
| * Change CPU count | |
| * Change Memory | |
| * Change Settings | |
| * Change Swapfile placement | |
| * Change resource | |
| * Configure Host USB device | |
| * Configure Raw device | |
| * Configure managedBy | |
| * Display connection settings | |
| * Extend virtual disk | |
| * Modify device settings | |
| * Query Fault Tolerance compatibility | |
| * Query unowned files | |
| * Reload from path | |
| * Remove disk | |
| * Rename | |
| * Reset guest information | |
| * Set annotation | |
| * Toggle disk change tracking | |
| * Toggle fork parent | |
| * Upgrade virtual machine compatibility | |
| Edit Inventory | |
| * Create from existing | |
| * Create new | |
| * Move | |
| * Register | |
| * Remove | |
| * Unregister | |
| Guest operations | |
| * Guest operation alias modification | |
| * Guest operation alias query | |
| * Guest operation modifications | |
| * Guest operation program execution | |
| * Guest operation queries | |
| Interaction | |
| * Console interaction | |
| * Power off | |
| * Power on | |
| Provisioning | |
| * Allow disk access | |
| * Allow file access | |
| * Allow read-only disk access | |
| * Allow virtual machine download | |
| * Allow virtual machine files upload | |
| * Clone template | |
| * Clone virtual machine | |
| * Create template from virtual machine | |
| * Customize guest | |
| * Deploy template | |
| * Mark as template | |
| * Mark as virtual machine | |
| * Modify customization specification | |
| * Promote disks | |
| * Read customization specifications | |
| Service configuration | |
| * Allow notifications | |
| * Allow polling of global event notifications | |
| * Manage service configurations | |
| * Modify service configuration | |
| * Query service configurations | |
| * Read service configuration | |
| Snapshot management | |
| * Create snapshot | |
| * Remove snapshot | |
| * Rename snapshot | |
| * Revert to snapshot | |
| vSphere Replication | |
| * Configure replication | |
| * Manage replication | |
| * Monitor replication | |
| vSAN | Cluster |
| ShallowRekey |
Root-Level Role Privileges
Root-level role privileges listed in the table are applied only to root object and data center objects.
| vSphere Object | Privileges |
|---|---|
| Cns | Searchable |
| Datastore | Browse datastore |
| Host | Configuration |
| * Storage partition configuration | |
| vSphere Tagging | Create vSphere Tag |
| Edit vSphere Tag | |
| Network | Assign network |
| Sessions | Validate session |
| Profile-driven storage | Profile-driven storage view |
| Storage views | View |
Spectro Role Privileges
The Spectro role privileges listed in the table must be applied to the spectro-template folder, hosts, clusters, virtual machines, templates, datastore, and network objects.
Palette downloads images and Open Virtual Appliance (OVA) files to the spectro-templates folder and clones images from it to create nodes.
| vSphere Object | Privileges |
|---|---|
| spectro-templates | Read only |
| Cns | Searchable |
| Datastore | Allocate space |
| Browse datastore | |
| Low level file operations | |
| Remove file | |
| Update virtual machine files | |
| Update virtual machine metadata | |
| Folder | Create folder |
| Delete folder | |
| Move folder | |
| Rename folder | |
| Host | Local operations |
| Reconfigure virtual machine | |
| vSphere Tagging | Assign or Unassign vSphere Tag |
| Create vSphere Tag | |
| Delete vSphere Tag | |
| Edit vSphere Tag | |
| Network | Assign network |
| Resource | Apply recommendation |
| Assign virtual machine to resource pool | |
| Migrate powered off virtual machine | |
| Migrate powered on virtual machine | |
| Query vMotion | |
| Sessions | Validate session |
| Profile-driven storage | Profile-driven storage view |
| Storage views | Configure service |
| View | |
| Tasks | Create task |
| Update task | |
| vApp | Export |
| Import | |
| View OVF environment | |
| vApp application configuration | |
| vApp instance configuration | |
| Virtual machines | Change Configuration |
| * Acquire disk lease | |
| * Add existing disk | |
| * Add new disk | |
| * Add or remove device | |
| * Advanced configuration | |
| * Change CPU count | |
| * Change Memory | |
| * Change Settings | |
| * Change Swapfile placement | |
| * Change resource | |
| * Configure Host USB device | |
| * Configure Raw device | |
| * Configure managedBy | |
| * Display connection settings | |
| * Extend virtual disk | |
| * Modify device settings | |
| * Query Fault Tolerance compatibility | |
| * Query unowned files | |
| * Reload from path | |
| * Remove disk | |
| * Rename | |
| * Reset guest information | |
| * Set annotation | |
| * Toggle disk change tracking | |
| * Toggle fork parent | |
| * Upgrade virtual machine compatibility | |
| Edit Inventory | |
| * Create from existing | |
| * Create new | |
| * Move | |
| * Register | |
| * Remove | |
| * Unregister | |
| Guest operations | |
| * Guest operation alias modification | |
| * Guest operation alias query | |
| * Guest operation modifications | |
| * Guest operation program execution | |
| * Guest operation queries | |
| Interaction | |
| * Console interaction | |
| * Power off | |
| * Power on | |
| Provisioning | |
| * Allow disk access | |
| * Allow file access | |
| * Allow read-only disk access | |
| * Allow virtual machine download | |
| * Allow virtual machine files upload | |
| * Clone template | |
| * Clone virtual machine | |
| * Create template from virtual machine | |
| * Customize guest | |
| * Deploy template | |
| * Mark as template | |
| * Mark as virtual machine | |
| * Modify customization specification | |
| * Promote disks | |
| * Read customization specifications | |
| Service configuration | |
| * Allow notifications | |
| * Allow polling of global event notifications | |
| * Manage service configurations | |
| * Modify service configuration | |
| * Query service configurations | |
| * Read service configuration | |
| Snapshot management | |
| * Create snapshot | |
| * Remove snapshot | |
| * Rename snapshot | |
| * Revert to snapshot | |
| vSphere Replication | |
| * Configure replication | |
| * Manage replication | |
| * Monitor replication | |
| vSAN | Cluster |
| ShallowRekey |
Root-Level Role Privileges
Root-level role privileges listed in the table are applied only to root object and data center objects.
| vSphere Object | Privileges |
|---|---|
| Cns | Searchable |
| Datastore | Browse datastore |
| Host | Configuration |
| * Storage partition configuration | |
| vSphere Tagging | Create vSphere Tag |
| Edit vSphere Tag | |
| Network | Assign network |
| Sessions | Validate session |
| Profile-driven storage | Profile-driven storage view |
| Storage views | View |
Spectro Role Privileges
The Spectro role privileges listed in the table must be applied to the spectro-template folder, hosts, clusters, virtual machines, templates, datastore, and network objects.
Palette downloads images and Open Virtual Appliance (OVA) files to the spectro-templates folder and clones images from it to create nodes.
| vSphere Object | Privileges |
|---|---|
| spectro-templates | Read only |
| Cns | Searchable |
| Datastore | Allocate space |
| Browse datastore | |
| Low level file operations | |
| Remove file | |
| Update virtual machine files | |
| Update virtual machine metadata | |
| Folder | Create folder |
| Delete folder | |
| Move folder | |
| Rename folder | |
| Host | Local operations |
| Reconfigure virtual machine | |
| vSphere Tagging | Assign or Unassign vSphere Tag |
| Create vSphere Tag | |
| Delete vSphere Tag | |
| Edit vSphere Tag | |
| Network | Assign network |
| Resource | Apply recommendation |
| Assign virtual machine to resource pool | |
| Migrate powered off virtual machine | |
| Migrate powered on virtual machine | |
| Query vMotion | |
| Sessions | Validate session |
| Profile-driven storage | Profile-driven storage view |
| Storage views | Configure service |
| View | |
| Tasks | Create task |
| Update task | |
| vApp | Export |
| Import | |
| View OVF environment | |
| vApp application configuration | |
| vApp instance configuration | |
| Virtual machines | Change Configuration |
| * Acquire disk lease | |
| * Add existing disk | |
| * Add new disk | |
| * Add or remove device | |
| * Advanced configuration | |
| * Change CPU count | |
| * Change Memory | |
| * Change Settings | |
| * Change Swapfile placement | |
| * Change resource | |
| * Configure Host USB device | |
| * Configure Raw device | |
| * Configure managedBy | |
| * Display connection settings | |
| * Extend virtual disk | |
| * Modify device settings | |
| * Query Fault Tolerance compatibility | |
| * Query unowned files | |
| * Reload from path | |
| * Remove disk | |
| * Rename | |
| * Reset guest information | |
| * Set annotation | |
| * Toggle disk change tracking | |
| * Toggle fork parent | |
| * Upgrade virtual machine compatibility | |
| Edit Inventory | |
| * Create from existing | |
| * Create new | |
| * Move | |
| * Register | |
| * Remove | |
| * Unregister | |
| Guest operations | |
| * Guest operation alias modification | |
| * Guest operation alias query | |
| * Guest operation modifications | |
| * Guest operation program execution | |
| * Guest operation queries | |
| Interaction | |
| * Console interaction | |
| * Power off | |
| * Power on | |
| Provisioning | |
| * Allow disk access | |
| * Allow file access | |
| * Allow read-only disk access | |
| * Allow virtual machine download | |
| * Allow virtual machine files upload | |
| * Clone template | |
| * Clone virtual machine | |
| * Create template from virtual machine | |
| * Customize guest | |
| * Deploy template | |
| * Mark as template | |
| * Mark as virtual machine | |
| * Modify customization specification | |
| * Promote disks | |
| * Read customization specifications | |
| Service configuration | |
| * Allow notifications | |
| * Allow polling of global event notifications | |
| * Manage service configurations | |
| * Modify service configuration | |
| * Query service configurations | |
| * Read service configuration | |
| Snapshot management | |
| * Create snapshot | |
| * Remove snapshot | |
| * Rename snapshot | |
| * Revert to snapshot | |
| vSphere Replication | |
| * Configure replication | |
| * Manage replication | |
| * Monitor replication | |
| vSAN | Cluster |
| ShallowRekey |
Create VMware Cloud Gateway
You can use two different PCG installation methods for VMware vSphere. You can use the Palette CLI, or you can use an OVA/OVF template. Review the prerequisites for each option to help you identify the correct installation method.
- Palette CLI
- OVA/OVF Template
Prerequisites
- Palette version 4.0.X or greater.
- A Palette API key. Refer to the Create API Key page for guidance.
Download the Palette CLI from the Downloads page and install the CLI. Refer to the Palette CLI Install guide to learn more.
You can set up the PCG as a single or three-node cluster based on your requirements for high availability (HA). The following t-shirt sizes are suggested for a VMware Private Cloud Gateway PCG. The PCG size impacts the maximum number of simultaneous cluster deployments.
Use the following tables to determine the appropriate PCG node resource size for your environment.
Single-Node Cluster
Size Nodes CPU Memory Storage Maximum concurrent cluster deployments S 1 4 4 GB 60 GB 1-3 M 1 8 8 GB 100 GB 4-6 L 1 16 16 GB 120 GB 7-10 High-Availability (HA) Cluster
Size Nodes CPU Memory Storage Maximum concurrent cluster deployments S 3 4 4 GB 60 GB 4-6 M 3 8 8 GB 100 GB 7-10 L 3 16 16 GB 120 GB 10-15 Sufficient available IP addresses within the configured vSphere subnets.
Self-hosted Palette installations provide a system PCG out-of-the-box and typically do not require a separate, user-installed PCG. However, you can create additional PCGs as needed to support provisioning into remote data centers that do not have a direct incoming connection from the management console.
Install PCG
- In an x86 Linux host, open up a terminal session.
Use the Palette CLI
logincommand to authenticate the CLI with Palette. When prompted, enter the information listed in the following table.palette loginParameter Description Spectro Cloud Console Enter the Palette endpoint URL. When using the Palette SaaS service, enter https://console.spectrocloud.com. When using a self-hosted instance of Palette, enter the URL for that instance.Allow Insecure Connection Enabling this option bypasses x509 verification. Enter yif you are using a self-hosted Palette instance with self-signed TLS certificates. Otherwise, entern.Spectro Cloud API Key Enter your Palette API Key. Spectro Cloud Organization Enter your Palette Organization name. Spectro Cloud Project Enter your desired project name within the selected Organization.
Once you have authenticated successfully, invoke the PCG installer by issuing the following command. When prompted, enter the information listed in each of the following tables.
palette pcg installParameter Description Cloud Type Choose VMware vSphere. Private Cloud Gateway Name Enter a custom name for the PCG. Example: vmware-pcg-1.Share PCG Cloud Account across platform Projects Enter yif you want the Cloud Account associated with the PCG to be available from all projects within your organization. Enternif you want the Cloud Account to only be available at the tenant admin scope.
Next, provide environment configurations for the cluster. Refer to the following table for information about each option.
Parameter Description HTTPS Proxy Leave this blank unless you are using an HTTPS Proxy. This setting will be propagated to all PCG nodes and all of its cluster nodes. Example: https://USERNAME:PASSWORD@PROXYIP:PROXYPORT.HTTP Proxy Leave this blank unless you are using an HTTP Proxy. This setting will be propagated to all PCG nodes and all of its cluster nodes. Example: http://USERNAME:PASSWORD@PROXYIP:PROXYPORT.No Proxy You will be prompted to provide a list of local network CIDR addresses, hostnames, and domain names that should be excluded from being a proxy. This setting will be propagated to all the nodes to bypass the proxy server. Example if you have a self-hosted environment: my.company.com,10.10.0.0/16.Proxy CA Certificate Filepath The default is blank. You can provide the file path of a CA certificate on the installer host. If provided, this CA certificate will be copied to each host in the PCG cluster during deployment. The provided path will be used on the PCG cluster hosts. Example: /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/ca.crt.Pod CIDR Enter the CIDR pool that will be used to assign IP addresses to pods in the PCG cluster. The pod IP addresses should be unique and not overlap with any machine IPs in the environment. Service IP Range Enter the IP address range that will be used to assign IP addresses to services in the PCG cluster. The service IP addresses should be unique and not overlap with any machine IPs in the environment.
After the environment options, the next set of prompts is for configuring the PCG cluster for the VMware environment. The following table contains information about each prompt.
Parameter Description vSphere Endpoint vSphere endpoint: FQDN or IP address, without the HTTP scheme https://orhttp://.
Example:vcenter.mycompany.comvSphere Username vSphere account username. vSphere Password vSphere account password. Allow Insecure Connection Enabling this option bypasses x509 verification. Enter yif using a vSphere instance with self-signed TLS certificates. Otherwise, entern.
Next, fill out VMware account configurations. Specify values for the following properties.
Parameter Description Datacenter The data center to target when deploying the PCG cluster. Folder The folder to target when deploying the PCG cluster. Fault Domains Specify any fault domains you would like to use. Cluster The compute cluster to use for the PCG deployment. Network The port group the PCG cluster will be connected to. Resource Pool The resource pool to target when deploying the PCG cluster. Storage Type Select the datastore or VM Storage policy to apply to the PCG cluster. NTP Servers Specify the IP address for any Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers the PCG cluster can reference. SSH Public Keys Provide the public OpenSSH key for the PCG cluster. Use this key when establishing an SSH connection with the PCG cluster. This prompt will result in the default text editor for the Operating System to open. Vi is the more common text editor used in Linux environments. Cluster Size The number of nodes that will make up the cluster. Available options are 1 or 3 . Use three nodes for a High Availability (HA) cluster.
Specify IP Pool configuration. You have the option to select a static placement or use Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS). With static placement, an IP pool is created and the PCG VMs are assigned IP addresses from the selected pool. With DDNS, PCG VMs are assigned IP addresses via DNS. Review the following tables to learn more about each parameter.
Static Placement Configuration
Parameter Description IP Start range Enter the first address in the PCG IP pool range. IP End range Enter the last address in the PCG IP pool range. Network Prefix Enter the network prefix for the IP pool range. Valid values are network CIDR subnet masks from the range 0 - 32. Example:18.Gateway IP Address Enter the IP address of the IP gateway. Name servers Comma-separated list of DNS name server IP addresses. Name server search suffixes (optional) Comma-separated list of DNS search domains. DDNS Placement Configuration
Parameter Description Search domains Comma-separated list of DNS search domains.
Specify the cluster boot configuration.
Parameter Description Patch OS on boot This parameter indicates whether or not to patch the OS of the PCG hosts on the first boot. Reboot nodes once OS patch is applied This parameter indicates whether or not to reboot PCG nodes after OS patches are complete. This only applies if the Patch OS on boot parameter is enabled.
Enter the vSphere Machine configuration for the Private Cloud Gateway.
Parameter Description CPU The number of CPUs in the Virtual Machine. Memory The number of memory to allocate to the Virtual Machine. Storage The amount of storage to allocate to the Virtual Machine. A new PCG configuration file is generated and its location is displayed on the console. You will receive an output similar to the following.
==== PCG config saved ====
Location: :/home/demo/.palette/pcg/pcg-20230706150945/pcg.yamlinfoThe
CloudAccount.apiKeyandMgmt.apiKeyvalues in the pcg.yaml are encrypted and cannot be manually updated. To change these values, restart the installation process using thepalette pcg installcommand.
The Palette CLI will now provision a PCG cluster in your VMware environment. If the deployment fails due to misconfiguration, update the PCG configuration file and restart the installer. Refer to the Edit and Redeploy PCG section below. For additional assistance, visit our Customer Support portal.
Validate
Once installed, the PCG registers itself with Palette. To verify the PCG is registered, use the following steps.
- Log in to Palette as a tenant admin.
- Navigate to the left Main Menu and select Tenant Settings
- From the Tenant Settings Menu click on Private Cloud Gateways. Verify your PCG cluster is available from the list of PCG clusters displayed.
Edit and Redeploy PCG
To change the PCG install values, restart the installation process using the palette pcg install command. Use the following steps to redeploy the PCG or restart the install process.
Make the necessary changes to the PCG configuration file the CLI created during the installation, if needed. Use a text editor, such as vi or nano to update the PCG install configuration file.
==== Create PCG reference config ====
==== PCG config saved ====
Location: /Users/demo/.palette/pcg/pcg-20230717114807/pcg.yamlvi /home/demo/.palette/pcg/pcg-20230706150945/pcg.yaml
To redeploy the PCG, use the
installcommand with the flag--config-file. Provide the file path to the generated PCG config file that was generated and displayed in the output.palette pcg install --config-file /home/demo/.palette/pcg/pcg-20230706150945/pcg.yaml
PCG Install With OVA/OVF
The following points give an overview of what you will do to set up the PCG:
- Initiate the installation from the tenant portal.
- Deploy the gateway installer VM in VMware vSphere.
- Launch the cloud gateway from the tenant portal.
Self-hosted Palette installations provide a system gateway out-of-the-box and typically do not require a PCG. However, you can create additional gateways as needed to support provisioning into remote data centers that do not have a direct incoming connection from the management console.
Prerequisites
- Palette version 3.4.X or older.
You can set up the PCG as a single- or three-node cluster based on your requirements for high availability (HA). The minimum PCG resource requirements are the following.
Single-node cluster: 2 vCPU, 4 GB memory, 60 GB storage.
High-Availability (HA) three-node cluster: 6 vCPU, 12 GB memory, 70 GB storage.
Install PCG
- Log in to Palette as a tenant admin.
- Navigate to the left Main Menu and select Tenant Settings > Private Cloud Gateway.
- Click the Create Private Cloud Gateway button and select VMware. Private Gateway installation instructions are displayed.
- Copy the gateway-installer link. Alternatively, you can download the OVA and upload it to an accessible location and import it as a local file.
vSphere - Deploy Gateway Installer
- Deploy a new OVF template by providing the link to the installer OVA as the URL.
- Proceed through the OVF deployment wizard, selecting the desired Name, Placement, Compute, Storage, and Network options.
- At the Customize Template step, specify Palette properties as follows:
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Installer Name | Desired Palette Gateway Name. | The name will be used to identify the gateway instance. Typical environments may only require a single gateway to be deployed. However, multiple gateways may be required to manage clusters across multiple vCenters. We recommend choosing a name that readily identifies the environment for which this gateway instance is being configured. |
| Console endpoint | URL to Palette management platform portal. | Default: https://console.spectrocloud.com |
| Pairing Code | PIN displayed on the Palette management platform portal's 'Create a new gateway' dialogue. | |
| SSH Public Key | Optional key for troubleshooting purposes. | We recommended having an SSH key, as it enables SSH access to the VM as 'ubuntu' user. |
| Pod CIDR | Optional IP range exclusive to pods. | This range should be different to prevent an overlap with your network CIDR. |
| Service cluster IP range | Optional IP range in the CIDR format exclusive to the service clusters. | This range also must not overlap with either the pod CIDR or your network CIDR. |
Proxy environments require additional property settings. Each of the proxy properties may or may not have the same value but all the three properties are required.
| Parameter | Value | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP PROXY | Endpoint for the HTTP proxy server. | This setting will be propagated to all the nodes launched in the proxy network. For example: http://USERNAME:PASSWORD@PROXYIP:PROXYPORT |
| HTTPS PROXY | Endpoint for the HTTPS proxy server. | This setting will be propagated to all the nodes launched in the proxy network. For example: http://USERNAME:PASSWORD@PROXYIP:PROXYPORT |
| NO Proxy | A comma-separated list of vCenter server, local network CIDR, hostnames, and domain names that should be excluded from proxying. | This setting will be propagated to all the nodes to bypass the proxy server. For example: vcenter.company.com, .company.org, and 10.10.0.0/16 |
| Certificate | The base64-encoded value of the proxy server's certificate OR the base64-encoded root and issuing certificate authority (CA) certificates used to sign the proxy server's certificate. | Depending on how the certificate is decoded, an additional = character may appear at the end of the value. You can use this command to properly encode the certificate: base64 -w0 | sed "s/=$//". |
- Complete the OVF deployment wizard and wait for the OVA to be imported and the Virtual Machine (VM) to be deployed.
- Power on the VM.
Tenant Portal - Launch Cloud Gateway
- Close the Create New Gateway installation instructions and navigate to the Private Cloud Gateway page under Tenant Settings if you have navigated away or logged out.
- Wait for a gateway widget to display on the page and for the Configure option to become available. The IP address of the installer VM will be displayed on the gateway widget. This may take a few minutes after the VM is powered on. Failure of the installer to register with Palette within 10 minutes of powering on the Virtual Machine on vSphere might indicate an error. Follow steps in Troubleshooting to identify and resolve the issue.
- Click on the Configure button to invoke the Palette Configuration dialogue. Provide vCenter credentials and proceed to the next configuration step.
Choose the desired values for the Data Center, Compute Cluster, Datastore, Network, Resource pool, and Folder. Optionally, provide one or more SSH Keys or NTP server addresses.
Virtual machine port groups and distributed port groups are listed with their names. NSX-T distributed virtual port groups that exist in vSphere will be listed with their name and segment IDs.
- Choose the IP Allocation Scheme - Static IP or DHCP. Selecting static IP enables the option to create an IP pool. To create an IP pool, provide an IP range or a subnet. The IP addresses from the IP pool will be assigned to the gateway cluster. By default, the IP pool is available for use by other tenant clusters. You can prevent this by toggling on the Restrict to a single cluster option.
Click on Confirm to initiate gateway cluster provisioning. Cluster status should change to Provisioning and eventually to Running, when the gateway cluster is fully provisioned. This process can take about 10 minutes.
You can click on the Cloud Gateway widget in the UI to view a detailed provisioning sequence on the Cluster Details page. If gateway cluster provisioning results in errors or gets stuck, you can view the details on the Summary tab or the Events tab of the Cluster Details page.
In certain cases where provisioning of the gateway cluster is stuck or failed due to invalid configuration, you can reset the process from the Cloud Gateway widget.
- When the Gateway transitions to the Running state, it is fully provisioned and ready to bootstrap tenant cluster requests.
- Power off the installer OVA that you initially imported at the start of this installation process.
A Gateway cluster installation automatically creates a cloud account using the credentials entered at the time the gateway cluster is deployed. You can use this account to provision clusters across all tenant projects.
Upgrade PCG
Palette maintains the OS image and all configurations for the cloud gateway. Periodically, the OS images, configurations, or other components need to be upgraded to resolve security or functionality issues. Palette releases such upgrades when required and communication about the same is presented in the form of an upgrade notification on the gateway.
Administrators should review the changes and apply them at a suitable time. Upgrading a cloud gateway does not result in any downtime for the Tenant Clusters. During the upgrade process, the provisioning of new clusters might be temporarily unavailable. New cluster requests are queued while the gateway is being upgraded and are processed as soon as the gateway upgrade is complete.
Delete a VMware Cloud Gateway
The following steps need to be performed to delete a cloud gateway:
- As a Tenant Administrator, navigate to the Private Cloud Gateway page under Settings.
- Invoke the Delete action on the PCG instance you want to delete.
- The system performs a validation to ensure there are no running tenant clusters associated with the PCG instance being deleted. If such instances are found, an error is displayed. Delete any running tenant clusters and retry deleting the PCG.
- Delete the Gateway Virtual Machines from vSphere.
Resize PCG
You can set up the PCG as a single-node cluster or as a three-node cluster for high availability (HA). For production environments, we recommend three nodes. A PCG can be initially set up with one node and resized to three nodes later. Use the following steps to resize a single-node PCG cluster to a three-node PCG cluster.
- As a Tenant Administrator, navigate to the Private Cloud Gateway page under Settings.
- Invoke the resize action for the relevant cloud gateway instance.
- Update the size from one (1) to three (3).
- The gateway upgrade begins shortly after the update. Two new nodes are created on vSphere and the gateway is upgraded to a 3-node cluster.
Scaling a 3-node cluster down to a 1-node cluster is not permitted.
A load balancer instance is launched even for a 1-node gateway to support future expansion.IP Address Management
Palette supports both DHCP and Static IP-based allocation strategies for the VMs that are launched during cluster creation. IP Pools can be defined using a range or a subnet. Administrators can define one or more IP pools linked to a PCG.
Clusters created using a PCG can select from the IP pools linked to the corresponding PCG. By default, IP Pools are shared across multiple clusters but can optionally be restricted to a cluster.
The following is a description of various IP Pool properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Descriptive name for the IP Pool. This name will be displayed for IP Pool selection when static IP is chosen as the IP allocation strategy |
| Network Type | Select Range to provide a start and an end IP address. IPs within this range will become part of this pool. Alternately select 'Subnet' to provide the IP range in CIDR format. |
| Start | First IP address for a range based IP Pool E.g. 10.10.183.1 |
| End | Last IP address for a range based IP Pool. E.g. 10.10.183.100 |
| Subnet | CIDR to allocate a set of IP addresses for a subnet based IP Pool. E.g. 10.10.183.64/26 |
| Subnet Prefix | Network subnet prefix. e.g. /18 |
| Gateway | Network Gateway E.g. 10.128.1.1 |
| Name server addresses | A comma-separated list of name servers. e.g., 8.8.8.8 |
| Restrict to a Single Cluster | Select this option to reserve the pool for the first cluster that uses this pool. By default, IP pools can be shared across clusters. |
Create a VMware Cloud Account
Use the following steps to create a VMware cloud account.
Prerequisites
A VMware cloud gateway must be configured. Refer to the Create VMware Cloud Gateway section for guidance.
infoEnterprise version users should choose the Use System Gateway option.
In addition to the default cloud account already associated with the private cloud gateway, new user cloud accounts can be created for the different vSphere users.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Account Name | Custom name for the cloud account |
| Private cloud gateway | Reference to a running cloud gateway |
| vCenter Server | IP or FQDN of the vCenter server |
| Username | vCenter username |
| Password | vCenter password |
If you change the password for a user account in vCenter, you must also change it in Palette for the same VMware cloud account. We recommend updating the passwords immediately to avoid potentially locking Palette out of vCenter. For guidance, refer to Change VMware Cloud Account Password in Palette.
Change VMware Cloud Account Password
The user account password in vCenter must match the password for the corresponding VMware cloud account in Palette. This section provides steps to change the password in Palette in the event the vCenter password changes.
Prerequisites
- Access to the vCenter credentials.
Change the Password in Palette
Log in to Palette.
From the Menu Menu navigate to Tenant Settings > Cloud Accounts.
Click the three-dot Menu for the VMware account you want to update, and select Edit.
In the window that opens, update the password in the Password field and click the Validate button.
Confirm your changes.
Validation
Palette validates the password. Incorrect credentials will result in an error. As an extra precaution, try scaling a cluster up or down.
In addition to changing the password for a VMware account, Palette provides a way for you to also change the user associated with an account by entering a new username in the Username field. Ensure the new user account has the same permissions as the previous user account in vCenter.
Deploy a VMware Cluster
Use the following steps to provision a new VMware cluster.
- Provide the basic cluster information like Name, Description, and Tags. Tags are currently not propagated to the Virtual Machines (VMs) deployed on the cloud/data center environments.
- Select a Cluster Profile created for the VMware environment. The profile definition will be used as the cluster construction template.
- Review and override Pack Parameters as desired. By default, parameters for all Packs are set with values defined in the Cluster Profile.
Provide a vSphere Cloud account and placement information.
Parameter Description Cloud Account Select the desired cloud account.
VMware cloud accounts with credentials need to be preconfigured
in the Project Settings section. An account is auto-created as
part of the cloud gateway setup and is available for
provisioning of Tenant Clusters if permitted by the administrator.Datacenter The vSphere data center where the cluster nodes will be launched. Deployment Folder The vSphere VM Folder where the cluster nodes will be launched. Image Template Folder The vSphere folder to which the Spectro templates are imported. SSH Keys (Optional) Public key to configure remote SSH access to the nodes (User: spectro). NTP Server (Optional) Setup time synchronization for all the running nodes. IP Allocation strategy DHCP or Static IP Configure the master and worker node pools. Fill out the input fields in the Add node pool page. The following table contains an explanation of the available input parameters.
Master Pool
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | A descriptive name for the node pool. |
| Size | Number of VMs to be provisioned for the node pool. For the master pool, this number can be 1, 3, or 5. |
| Allow worker capability | Select this option for allowing workloads to be provisioned on master nodes. |
| Labels | Add a label to apply placement constraints on a pod, such as a node eligible for receiving the workload. |
| Taints | To set toleration to pods and allow (but do not require) the pods to schedule onto nodes with matching taints. |
| Instance type | Select the compute instance type to be used for all nodes in the node pool. |
| Availability Zones | Choose one or more availability zones. Palette provides fault tolerance to guard against hardware failures, network failures, etc., by provisioning nodes across availability zones if multiple zones are selected. |
| Disk Size | Give the required storage size |
Worker Pool
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | A descriptive name for the node pool. |
| Enable Autoscaler | You can enable the autoscaler by toggling the Enable Autoscaler button. Autoscaler scales resources up and down between the defined minimum and maximum number of nodes to optimize resource utilization. |
| Set the scaling limit by setting the Minimum Size and Maximum Size, as per the workload the number of nods will scale up from minimum set value to maximum set value and the scale down from maximum set value to minimum set value | |
| Size | Number of VMs to be provisioned for the node pool. |
| Rolling Update | Rolling update has two available options. Review the Update Parameter table below for more details. |
| Labels | Add a label to apply placement constraints on a pod, such as a node eligible for receiving the workload. |
| Taints | To set toleration to pods and allow (but do not require) the pods to schedule onto nodes with matching taints. |
| Instance type | Select the compute instance type to be used for all nodes in the node pool. |
| Availability Zones | Choose one or more availability zones. Palette provides fault tolerance to guard against hardware failures, network failures, etc., by provisioning nodes across availability zones if multiple zones are selected. |
| Disk Size | Provide the required storage size |
- Review settings and deploy the cluster. Provisioning status with details of ongoing provisioning tasks is available to track progress.
New worker pools may be added if it is desired to customize certain worker nodes to run specialized workloads. As an example, the default worker pool may be configured with 4 CPUs, 8 GB of memory for general-purpose workloads, and another worker pool with 8 CPUs, 16 GB of memory for advanced workloads that demand larger resources.
Delete a VMware Cluster
The deletion of a VMware cluster results in the removal of all Virtual machines and associated storage disks created for the cluster. The following tasks need to be performed to delete a VMware cluster:
- Select the cluster to be deleted from the Cluster View page and navigate to the Cluster Overview page.
- Invoke the delete action available on the page: Cluster > Settings > Cluster Settings > Delete Cluster.
- Click Confirm to delete.
The Cluster Status is updated to Deleting while the Cluster Resources are being deleted. Provisioning status is updated with the ongoing progress of the delete operation. Once all resources are successfully deleted, the Cluster Status changes to Deleted and is removed from the list of Clusters.
The Delete action is only available for Clusters that are fully provisioned. For Clusters that are still in the process of being provisioned, Abort action is available to stop provisioning and delete all resources.
Force Delete a Cluster
A cluster stuck in the Deletion state can be force deleted by the user through the User Interface. The user can go for a force deletion of the cluster, only if it is stuck in a deletion state for a minimum of 15 minutes. Palette enables cluster force delete from the Tenant Admin and Project Admin scope.
To force delete a cluster:
- Log in to the Palette Management Console.
Navigate to the Cluster Details page of the cluster stuck in deletion mode.
If the deletion status is stuck for more than 15 minutes, click the Force Delete Cluster button from the Settings dropdown.
If the Force Delete Cluster button is not enabled, wait for 15 minutes. The Settings dropdown will give the estimated time for the auto-enabling of the Force Delete button.
If there are any cloud resources still on the cloud, the user should cleanup those resources before going for the force deletion.